目录
两个相同字符之间的最长子字符串
给你一个字符串 s,请你返回 两个相同字符之间的最长子字符串的长度 ,计算长度时不含这两个字符。如果不存在这样的子字符串,返回 -1 。
子字符串 是字符串中的一个连续字符序列。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/largest-substring-between-two-equal-characters
示例
输入:s = “cabbac”
输出:4
解释:最优的子字符串是 “abba” ,其他的非最优解包括 “bb” 和 "” 。
思路1
对每个字符,向后遍历字符串,遇到与当前字符一样的,则计算相同字符间的子字符串长度,保留最大值。
代码1
|
|
执行操作后字典序最小的字符串
给你一个字符串 s 以及两个整数 a 和 b 。其中,字符串 s 的长度为偶数,且仅由数字 0 到 9 组成。
你可以在 s 上按任意顺序多次执行下面两个操作之一:
- 累加:将 a 加到 s 中所有下标为奇数的元素上(下标从 0 开始)。数字一旦超过 9 就会变成 0,如此循环往复。例如,s = “3456” 且 a = 5,则执行此操作后 s 变成 “3951”。
- 轮转:将 s 向右轮转 b 位。例如,s = “3456” 且 b = 1,则执行此操作后 s 变成 “6345”。 请你返回在 s 上执行上述操作任意次后可以得到的 字典序最小 的字符串。
如果两个字符串长度相同,那么字符串 a 字典序比字符串 b 小可以这样定义:在 a 和 b 出现不同的第一个位置上,字符串 a 中的字符出现在字母表中的时间早于 b 中的对应字符。例如,“0158” 字典序比 “0190” 小,因为不同的第一个位置是在第三个字符,显然 ‘5’ 出现在 ‘9’ 之前。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lexicographically-smallest-string-after-applying-operations
示例
输入:s = “74”, a = 5, b = 1
输出:“24”
解释:执行操作如下:
初态:“74”
轮转:“47”
累加:“42”
轮转:“24"
无法获得字典序小于 “24” 的字符串。
思路1
暴力DFS尝试每种可能性。
代码1
|
|
无矛盾的最佳球队
假设你是球队的经理。对于即将到来的锦标赛,你想组合一支总体得分最高的球队。球队的得分是球队中所有球员的分数 总和 。
然而,球队中的矛盾会限制球员的发挥,所以必须选出一支 没有矛盾 的球队。如果一名年龄较小球员的分数 严格大于 一名年龄较大的球员,则存在矛盾。同龄球员之间不会发生矛盾。
给你两个列表 scores 和 ages,其中每组 scores[i] 和 ages[i] 表示第 i 名球员的分数和年龄。请你返回 所有可能的无矛盾球队中得分最高那支的分数 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/best-team-with-no-conflicts
示例
输入:scores = [1,2,3,5], ages = [8,9,10,1]
输出:6 解释:最佳的选择是前 3 名球员。
思路1
贪心+动态规划:先按分数升序排序,再按年龄升序排序,dp[i]表示前i个球员且选择第i个球员的最大分数。对每个dp[i],设初值为第i个球员的分数,向前遍历,遇到年龄小于等于第i个球员的第j个球员,有分数等于dp[j]+第i个球员的分数,取其中最大值作为dp[i]。
代码1
|
|
带阈值的图连通性
有 n 座城市,编号从 1 到 n 。编号为 x 和 y 的两座城市直接连通的前提是: x 和 y 的公因数中,至少有一个 严格大于 某个阈值 threshold 。更正式地说,如果存在整数 z ,且满足以下所有条件,则编号 x 和 y 的城市之间有一条道路:
- x % z == 0
- y % z == 0
- z > threshold
给你两个整数 n 和 threshold ,以及一个待查询数组,请你判断每个查询 queries[i] = [ai, bi] 指向的城市 ai 和 bi 是否连通(即,它们之间是否存在一条路径)。
返回数组 answer ,其中answer.length == queries.length 。如果第 i 个查询中指向的城市 ai 和 bi 连通,则 answer[i] 为 true ;如果不连通,则 answer[i] 为 false 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/graph-connectivity-with-threshold
示例
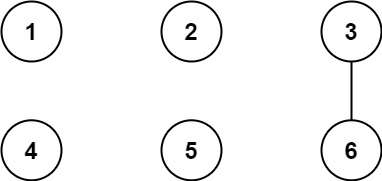
输入:n = 6, threshold = 2, queries = [[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]]
输出:[false,false,true]
解释:每个数的因数如下:
1: 1
2: 1, 2
3: 1, 3
4: 1, 2, 4
5: 1, 5
6: 1, 2, 3, 6
所有大于阈值的的因数已经加粗标识,只有城市 3 和 6 共享公约数 3 ,因此结果是:
[1,4] 1 与 4 不连通
[2,5] 2 与 5 不连通
[3,6] 3 与 6 连通,存在路径 3–6
思路1
并查集
代码1
|
|
总结
久不刷题,只能签到第1题了。